Oscillations
The world is amazing and diverse. We observe different body movements every day. We have all seen how a branch swings in the wind, a boat on the waves, a swing, trees in the wind. How do these movements differ from the movement of a cart moving in a straight line? We see that, unlike the movement of a cart moving in a straight line, the movements of all these bodies are repeated after a certain period of time.
Mechanical vibrations are physical processes that are exactly or approximately repeated at the same time intervals.
Fluctuations play a huge role in our lives. Examples of fluctuations in our body are the beating of the heart, the movement of the vocal cords. Fluctuations occur both in the life of our planet (tides, tides, earthquakes) and in astronomical phenomena (pulsations of stars). One of the terrible phenomena of nature is an earthquake — the oscillation of the Earth’s surface. Builders count on the structures they are building for earthquake stability.
Without knowledge of the laws of oscillation, it would be impossible to create television, radio and many modern devices and machines. Unaccounted fluctuations can lead to the destruction of complex technical structures and cause serious human diseases. All this makes their comprehensive study necessary.
The main feature of the oscillatory motion is its periodicity. An oscillating body passes the equilibrium position twice in one oscillation. The oscillations are characterized by such quantities as the period, frequency, amplitude and phase of the oscillations.
The amplitude is the largest displacement of the fluctuating magnitude from the equilibrium position.
At small amplitudes, the path traveled by the body in one complete oscillation is approximately four amplitudes.
The period of time during which a body makes one complete oscillation is called the oscillation period.
A period is the time of one complete oscillation.
To find the oscillation period, you need to divide the oscillation time by the number of oscillations.
T =t/N
The oscillation frequency is the number of oscillations per unit of time.
v=1/T
[v] = 1 Hz (hertz)
The frequency unit is named after the German scientist G. Hertz.
The oscillation phase is a physical quantity that determines the deviation of the oscillating quantity from the equilibrium position at a given time.
[ω] = 1 rad/ s
In all oscillatory systems, there are forces that strive to return the body to a state of stable equilibrium. There are several types of pendulums: thread and spring, etc. The word «pendulum» means a solid body capable of oscillating under the action of applied forces near a fixed point or around an axis.
We will consider spring and mathematical pendulums.
Spring pendulum. The oscillatory system in this case is a body attached to a spring. Vibrations in such a pendulum arise under the influence of the spring’s elastic force and gravity.
The oscillation period of the spring pendulum:
T is the oscillation period of the spring pendulum
m is the weight of the suspended load
𝑘 — spring stiffness
Mathematical pendulum.
A mathematical pendulum is a material point suspended on a long inextensible thread.
A mathematical pendulum is an idealized model. A real pendulum can be considered mathematical if the length of the thread is much larger than the size of the suspended body and the mass of the thread is negligible compared to the mass of the body. The oscillations of such a pendulum occur under the influence of thread tension and gravity. The formula for calculating the oscillation period of a mathematical pendulum was derived by Huygens.
T is the oscillation period of the mathematical pendulum
𝑙 – length of the pendulum thread
𝑔 — acceleration of free fall
Huygens proved that the period of small oscillations of the pendulum does not depend on time. Using this property, called the isochrony of the pendulum, Huygens designed the first pendulum clock in one thousand six hundred and fifty-seventh year. This property of the pendulum was discovered by the 19-year-old Galileo more than 20 years before Huygens’ discovery. Observing how the lamps suspended on threads of the same length swing in the cathedral, he noticed that their period of oscillation does not depend on time. There were no wristwatches then, and the young Galileo came to a decision that for many generations will serve as a model of the brilliance and wit of human thought: he compared the oscillations of a pendulum with the frequency of his own heartbeat.
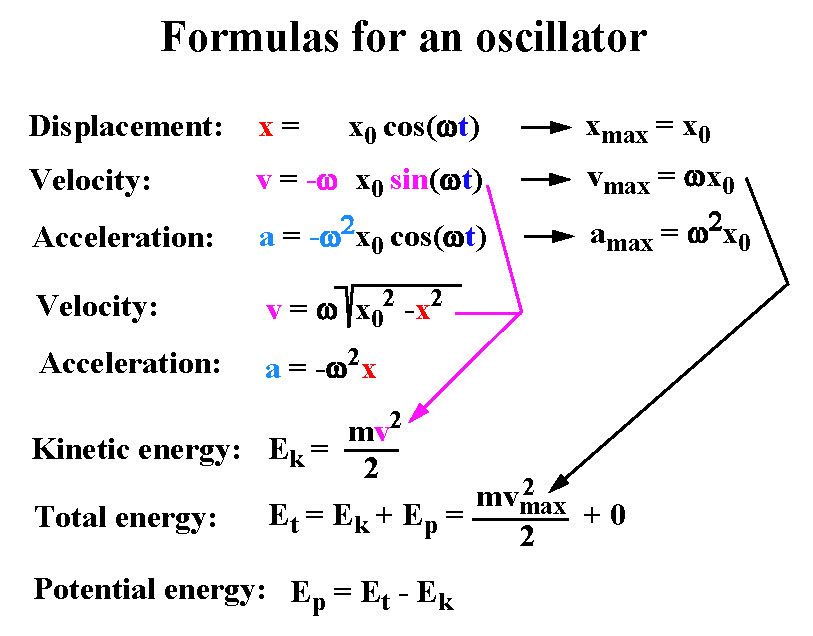
Harmonic vibrations are those that occur under the action of a force proportional to the displacement of the oscillating point and directed opposite to this displacement. The equation of harmonic oscillations:
x — coordinate of the fluctuating value
— the amplitude of the oscillations
ω — cyclic frequency
In the presence of frictional forces in the system, the vibrations are damped. The amplitude of the oscillations in this case decreases with time. Sometimes there is a need to dampen vibrations, for example, body vibrations, on springs when driving a car. Special shock absorbers are used to dampen vibrations. A piston is connected to the body, which, when oscillating, moves in a cylinder filled with liquid. A large resistance of the liquid leads to damping of vibrations.
Fluctuations occurring under the action of an external periodic force are called forced.
If the frequency of change of the external force is not equal to the frequency of free oscillations of the system, then the external force will not act in time with the free oscillations of the system itself. In this case, the amplitude of the oscillations will be determined by the maximum value of the external force acting on the system.
If the frequency of change of the external force coincides with the frequency of free oscillations, then there will be a sharp increase in the amplitude of the oscillations, since the external force in this case will act in time with the free oscillations of this system.
ω is the frequency of change of the external force.
ω0 is the frequency of free oscillations of the system.
The resonance phenomenon was first described by Galileo. The phenomenon of resonance plays an important role in nature, technology and science. Most structures and machines, having a certain elasticity, are able to make free oscillations. Therefore, external periodic impacts can cause their resonance, which can cause catastrophes. There are many cases when the source of dangerous fluctuations were people walking in step. So, in 1831, in the city of Manchester, when a column of soldiers marched across the bridge, the bridge collapsed. A similar case was in St. Petersburg in 1905. During the passage of the bridge over the Fontanka River by a squadron of Guards cavalry, the bridge collapsed. To prevent resonant phenomena, different methods of damping forced oscillations are used. One way is to change the frequency of free oscillations in the system. Another way is to increase the friction force in the system: the greater the friction force, the smaller the amplitude of the resonant vibrations